Mastering the Leg Press: Form, Benefits, and Common Mistakes
The leg press is one of the most well-liked workouts for developing lower body strength and muscle. Gaining proficiency with this machine will help you tone your legs, increase your endurance, and perform better regardless of your level of exercise experience. The several kinds of leg presses, correct form, typical errors, and safe training advice will all be covered in this article.
What is a Leg Press?
Leg press is a weight-training exercise that focuses mostly on the lower body. You extend your legs to push a weighted platform away from your body using specialized equipment. It works especially well for isolating the calves, quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes.
Benefits of the Leg Press
- Strength Development: Develops strong glutes, hamstrings, and quads.
- Toning lower body: helps to define the calves and thighs.
- Joint Support: Compared to free weights, joint support offers a controlled movement that is less taxing on the knees and back.
- Versatility: With movable weights and locations, it may be used by people of all fitness levels.
Main Muscles Worked
These muscles are the main ones worked by the leg press:
- Quadriceps: The muscles at the front of the leg that extend the knee are called the quadriceps.
- Hamstrings: The back thigh muscles known as the hamstrings help with hip extension and knee flexion.
- Glutes: When hip extension occurs, the buttock muscles contract.
- Calves: Pushing through your feet activates the muscles in your lower legs.
Types of Leg Presses
Two main types of equipment are available for doing the leg press workout, each of which has special advantages and targets distinct muscle groups:
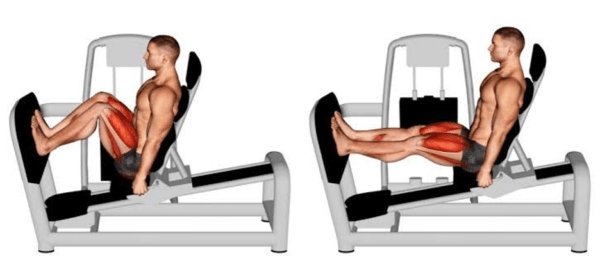
1) Horizontal Leg Press
With this equipment, a platform is pushed out horizontally and straight. It is easy to use and frequently found in gyms for beginners. Because it reduces back strain, the horizontal leg press is appropriate for people recuperating from injuries.
Benefits:
- Because of the upright seating position, it is easy on the lower back.
- Perfect for novices or anyone healing from injury.
- uses a limited range of motion to concentrate more on the quadriceps.
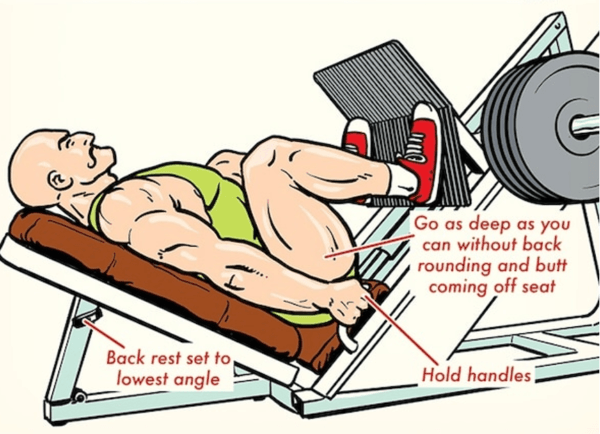
2) Incline Leg Press
The incline leg press has the platform raised upward. The challenge is increased when you push the weight diagonally. Because of its larger range of motion, this type, frequently found in elite gyms, provides better activation of the hamstrings and glutes.
Benefits:
- Engages a greater range of motion compared to the horizontal leg press.
- Targets the glutes and hamstrings more effectively.
- Preferred by experienced lifters aiming for a comprehensive lower body workout.
How to Do a Leg Press with Proper Form
Step-by-Step Guide
Setup: Sit on the machine with your back firmly against the backrest. Your feet should be shoulder-width apart on the platform.
Starting Position: Adjust the seat by adjusting your knees at a 90-degree angle. For stability, hold onto the side handles.
Execution: Extend your legs to push the platform away. Avoid locking your knees and maintain control of your motions.
Return: Without letting the weights rest, slowly bend your knees to return the platform to its initial position.
Workout Plan
This is an example of a strategy designed to help achieve three fitness objectives:
| Purpose | Repetition | Sets | Resting time |
| Building Strength | 6-8 | 4-5 | 90 sec |
| Muscular Endurance | 15-20 | 3-4 | 45 sec |
Leg Press Common Mistakes
At the peak of the exercise, locking your knees might cause joint strain and injury.
Raising Your Lower Back
If you allow your lower back to elevate off the seat, exercise efficiency can decrease, and injury risk can increase.
Inaccurate Foot Positioning
If your feet are positioned too high or too low on the platform, your knees will be under more stress, diverting attention from the targeted muscles.
The Machine Being Overloaded Knee Locking
Too much weight might throw off your form and make injuries more likely.
Reducing the Motion Range
Insufficient platform lowering can restrict muscle activation and diminish outcomes.
How to Work Out Safely and Avoid Injury
Warm-Up First: To warm up your muscles, start your workout with dynamic stretches or light aerobics.
Start Light: As your strength increases, the weight you use progressively increases.
Maintain Correct Form: To guarantee proper technique, follow the detailed instructions.
Pay Attention to Your Breathing: Take a breath out as you push the platform and a breath in as you return to the beginning.
Pay Attention to Your Body: Stop immediately if you feel pain or discomfort.
Final Thoughts
The leg press is an essential exercise for building a strong and well-toned lower body. With its ability to target the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves, it offers versatility for all fitness levels. Understanding the types of leg presses, mastering proper form, and following a structured plan are key to maximizing its benefits. You can guarantee efficiency and safety by avoiding typical errors like locking knees or overloading the machine. The leg press is a useful addition to any regimen, regardless of your goals toning, strength development, or endurance enhancement. Make good use of it and improve your fitness journey.
FAQs
-
What weight should I begin with when performing the leg press?
Choose a weight that will enable you to complete 12–15 repetitions with good form. Increase gradually as your strength increases.
-
Can a leg press take the place of a squat?
Leg presses are a fantastic substitute but don’t work the same stabilizing muscles as squats. Combine the two to create a well-rounded routine.
-
How frequently must I perform the leg press?
Try to do this two to three times a week, with a minimum of 48 hours off to allow for recovery.
-
Is it safe for beginners to perform the leg press?
Yes, the leg press is suitable for beginners. Begin with small weights and concentrate on perfecting the form.
-
How can I adjust the leg press to activate my glutes?
Place your feet higher on the platform to highlight your glutes throughout the exercise.











[…] leg press machine is a traditional substitute for hack squats, offering a comparable movement […]